Early learning goal – shape, space and measurement
Children use everyday language to talk about size, weight, capacity, position, distance, time and money in order to compare quantities, objects and solve problems. They recognise, create and describe patterns. They explore characteristics of everyday objects and shapes and use a mathematical language to describe them.
Through analysing the description of shapes, space and measures as described in the “EYFS Early Years Learning and Development Goals” it is clear that at nursery level children need to learn simple shapes such as triangles, quadrilaterals and circles. In addition to this they need to learn the relationships between these different shapes and how they fit into their surrounding environment. Most artificial objects are built on these simple shapes and complex shapes in nature can also be reflections of these. As well as this the compositions and constructions of shapes are widely used in the creative industries. Therefore at EYFS level it is particularly important to gradually improve children’s mathematical cognitive ability through different methods and activities.
In view of the age associated characteristics of children at EYFS level the following eight activities are recommended to promote a child’s recognition of shape and measurement.
Looking for shapes in the environment
Children are investigators by nature who enjoy “treasure hunts”. Teachers should support and help develop their interest in shape recognition by placing some pre-prepared two-dimensional shapes in various environments. The teacher then can lead the children to look for squares, circles, triangles, arcs and other shapes in their environment. This can enable the children to better understand shapes and their relationship to the child’s environment.
Potato shape printing
Potatoes are halved and cut into different shape stamps (such as squares and triangles). They are then applied with paint to be printed. Printing these potato shapes on paper will engage children as they can observe first hand and participate directly with enjoyment. This creative task is also a good way for children to discuss the shapes they have created with each other.
Car competition
This is a small scientific activity to develop a child’s ability to measure. The first step is to place a long cardboard tube at an angle making a slope and measure a long strip of paper of a fixed length to be secured at the bottom. The next step is to encourage children to take turns placing small cars at the top of the slope and observe how far they roll down the pipe and on to the paper below. Teachers can add numbers to the paper so that children can more easily measure the rolling distance of their cars.
Measuring the body
Measuring the body is an interesting and simple way to learn how to measure. This activity can be carried out indoors with large sheets of paper and pens or on the ground using chalk. Children can take turns lying on the ground and drawing shapes around each other. Following this, they can use rulers or tape to measure different body parts such as their arms, legs, feet, etc. Children can compare their measurements with their friends to improve their ability to interact and cooperate with each other.
Sorting size
This activity uses a variety of resources such as shells, buttons or dolls. A set of items of different sizes and three different jars or bowls are given to the children. They are then asked to classify these objects into small, medium and large sizes and put them in the corresponding bowl or jar. In this process, children learn to compare items to each other, before sorting them into the right bowl or jar.
Making shapes out of paper tape
Paper tape can be used to mark out large shapes on the floor. Children use building blocks such as Lego or toy bricks to cover the taped outline and thus create various shapes on the floor. This helps to better develop children’s shape recognition and measurement capabilities.
Continual sand supply in sandy area
Games involving sand and water are another great way to help children develop early measurement concepts. Nursery teachers and parents can both provide a variety of sand material and children must independently add to this when necessary. The process of checking that their sand supply is sustainable will help improve children’s mathematical ability. The game allows children to learn to compare different quantities all whilst enjoying the simple process of filling and emptying containers. They use everyday language to describe positions and when expressing size, so they gradually improve their perception of shape, space and measurement.
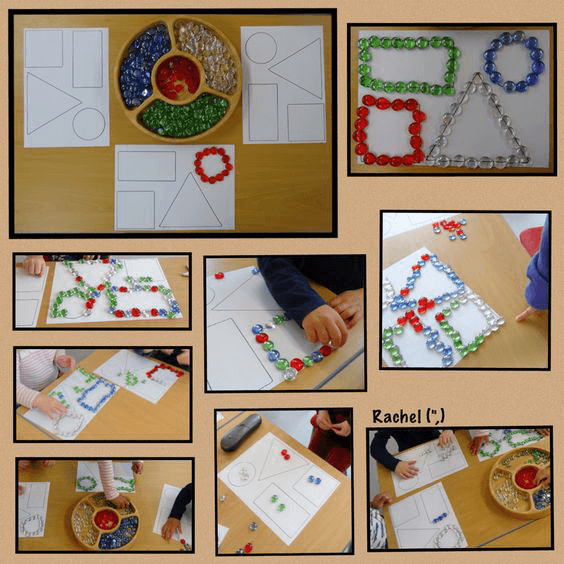
Collage game
Through creative collage games children’s perception of shape can be further enhanced. For this activity adults will need to cut lots of different shapes from various materials. Children then use these cut-outs to create shape combinations which may result in the creation of aliens, space rockets and many more images. Through these creative works (like the one pictured below) they learn to combine different shapes to create new and unique illustrations.
Additionally there are many more activities and methods to enhance children’s understanding of shape and ability to measure. The combination of learning about flat two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional spaces serves to better cultivate children’s overall perception of space, plane shape and measurement. Furthermore it is extremely important that early childhood teachers observe, record and reflect on each child’s development of shape, space and measurement.



